Botox is the number one aesthetic treatment provided worldwide by a large margin, so there is a good chance that you’ve heard of the name “Botox,” even if you are not familiar with what it does. So, what is Botox?
What is Botox?
Botox is a brand of FDA-approved injectable neurotoxin from Allergan Aesthetics that is designed to temporarily relax the muscles that cause frown lines. Botulinum toxin, the endotoxin that causes Botulism, is the origin of injectable Botox for aesthetic treatments. Botulism is the reason why you should never eat the contents of a swollen can and why you should never feed honey to infants. Botulinum toxin causes muscle paralysis by blocking the chemical signals that tell muscles when to contract. When used for aesthetic purposes, it temporarily relaxes the muscles involved in wrinkling the face. Other FDA-approved brands of botulinum toxin-derived neurotoxins with equivalent effects to Botox are: Dysport, Xeomin, Jeuveau, and the newest to market: Daxxify. All FDA-approved brands of injectable neurotoxins or neuromodulators are lab-created and administered in miniscule amounts in order to limit muscle relaxation effects to desired areas.

What is the difference between Botox, Dysport, Xeomin, Jeuveau, and Daxxify?
Botox, Dysport, Xeomin, Jeaveau, and Daxxify are different brands of FDA-approved injectable neurotoxins/neuromodulators. Each one is from a different pharmaceutical company, which means the specific botulinum toxin molecule and carrier molecule varies between each brand. Botox is from Allergan Aesthetics and is also the first-to-market brand. Because of this, the term “Botox” is almost synonymous with aesthetic neurotoxin treatments (like Kleenex or Xerox). Botox also has an accompanying “carrier” protein molecule bound to its botulinum toxin. Dysport is from Galderma Aesthetics and has a different constitution ratio, which makes dosing for Dysport different from all other brands. Xeomin is from Merz Aesthetics and is a pure botulinum toxin molecule with no carrier molecule. Jeuveau is from Evolus with a similar protein carrier to Dysport’s. Daxxify is the newest to market with a peptide carrier molecule, and is indicated to last up to 6 months. Because the botulinum toxin molecule is slightly different in each brand, dosing, diffusion from point of injection, and effective period varies depending on brand. Price may also vary between brands as well.
How does Botox work?
Botox works by preventing acetylcholine release at neuromuscular junctions, the meeting points between nerves & muscles. When you move a muscle, the brain initiates this process by sending a signal along a nerve to the muscles needed to perform a certain action. The neuromuscular junction is the meeting place between the nerve and muscle where nervous signals are translated into physical movements. By chemically-blocking communication between nerves and muscles, botulinum toxin temporarily relaxes the muscles where it is injected. The amount of neurotoxin injected in aesthetic treatments is very small, so this effect only lasts for a few months. Furthermore, this effect is localized to injected areas. Over time, repeated movement and contraction of muscles in the face can lead to wrinkles. Injection of neurotoxins in these areas prevents muscles from moving, softening existing wrinkles or even preventing wrinkle formation (only with early intervention, aka “preventative Botox”). If lines or wrinkles are visible even without animating the face (also known as “static lines”), Botox treatments can only soften these lines and prevent them from deepening with regular treatment. Botox treatments cannot get rid of static lines; additional adjunctive treatments such as fillers and/or laser treatments may be necessary for best results.
What areas can I treat with Botox?
FDA-approved areas that can be treated with Botox are the glabella (the area between the eyebrows), the forehead, as well as the crow’s feet. Dysport, Xeomin, Jeuveau, and Daxxify are FDA-approved for treatment of the glabella. FDA-approved areas are locations that have been clinically tested to be effectively treated by neurotoxins. Other common areas for aesthetic neurotoxin treatments are: the masseters for contouring the jawline/”slimming” the face, the nose for “bunny lines” when you scrunch your nose, DAO to treat downturned corners of the mouth, the upper lip to treat smoker’s lines or a gummy smile, a dimple-y chin when smiling, the neck for platysma bands, the calf muscles or trapezius muscles to slim these muscles, the nostrils to treat excessively flared nostrils, the underarms for hyperhydrosis (excessive sweating), and many other uses. Neuromodulators also have many medical applications as well, e.g. for sports medicine, in migraine treatments, TMJD, and more. They can also be hyperdiluted for “micro-Botox” treatments, wherein very small amounts are used to shrink large pores or to give skin a rejuvenated, shiny appearance.
What is a unit of Botox?
Botox is measured in “units,” which is an arbitrary measurement to designate the quantity used. All brands of neuromodulators are transported in crystalline or powder form for safety during shipping. When ready to be used, they are reconstituted with saline in order to be injectable. Thus, “units” refers to the active amount of neurotoxin in a given amount of solution, as the amount of saline necessary can vary between different brands and between different intended usages. Unit to unit, Botox, Xeomin, & Jeuveau are equivalent in terms of standard constitution. Units of Dysport differ because it has a different standard constitution ratio; therefore, Dysport units need to be multiplied by 2 – 2.5x in order to be equivalent to Botox, Xeomin, or Jeuveau units. Understanding that the term “units” may mean different dosages between brands is key to getting equivalent treatments when switching between brands.
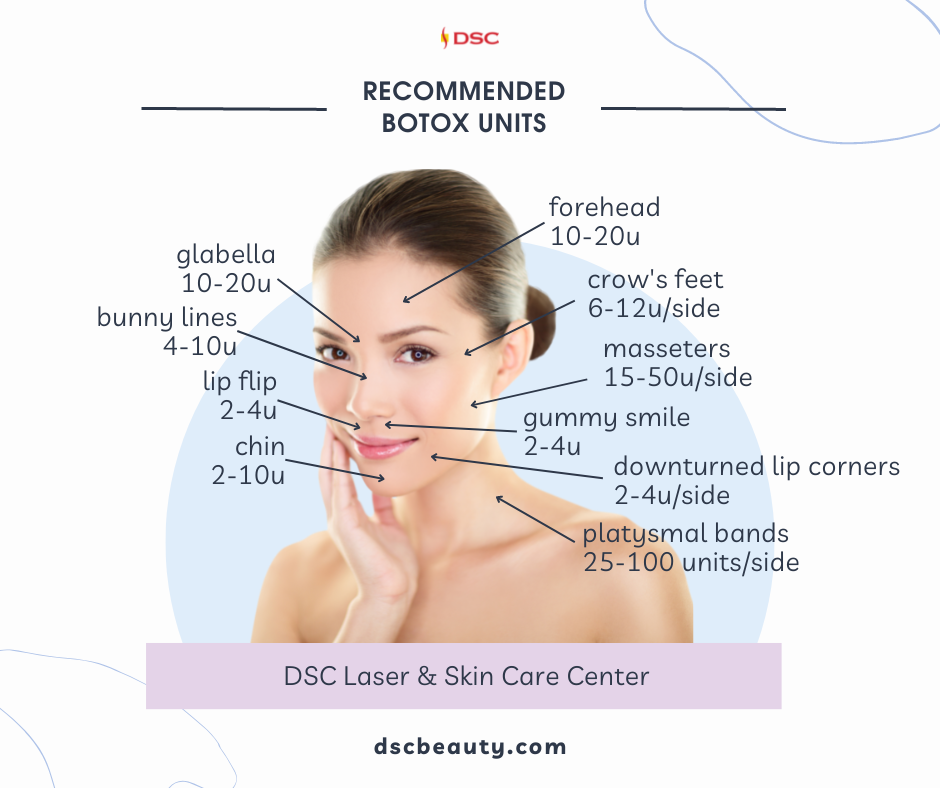
How much Botox do I need?
Each treatment area has a general standard range of recommended units necessary for effective treatment. This varies due to different anatomy, age, frequency of treatment, desired effect, and skin condition. Your provider can recommend a certain dosage and after 2 weeks, you can reassess to see if you are satisfied with the results. Again, units can also differ between brands, so dosing will vary.
How long does Botox last?
Botox is FDA-indicated to last up to 4 months. Different brands range between 3-4 months, so you can expect up to 3 or 4 treatments a year if treated regularly. Daxxify, the newest neuromodulator to market, is FDA-indicated to last up to 6 months. However, like dyeing your hair, how often you get treated is a personal preference and depends on your budget, lifestyle, and desired outcome.
How quickly does Botox begin to work?
While it differs between brands, neuromodulators usually need up to 2-3 weeks for full, maximal effect to be seen. Effects may begin to be visible as soon as a few days and will increase as time passes. Results will NOT be visible immediately post treatment. This is why it is always recommended to wait at least two to three weeks for reassessments or touchups.
What is the difference between fillers and Botox?
Neuromodulators like Botox and injectable fillers are often mixed up. While fillers and Botox are commonly used together in aesthetic treatments, the term “Botox” is often incorrectly used as a catch-all term for all injectable aesthetic treatments. As previously mentioned, neuromodulators like Botox temporarily relax muscles, which can lead to the softening of existing wrinkles and prevents them from deepening with regular treatment. Fillers are injectable gels of varying thicknesses, usually made of hyaluronic acid, that correct age-related loss of volume in the face or change the natural contours of the face. Filler is intended to change volume and therefore results are immediately visible (but swelling and “settling” may take days or weeks to resolve), while neuromodulators like Botox work chemically to relax muscles and therefore can take days or weeks to fully kick in.
Related: DSC Fillers
Who should not get Botox?
The main contraindications for Botox are pregnancy and breastfeeding. Other conditions that make Botox unsuitable are: Lou Gehrig’s disease, myasthenia gravis, peripheral motor neuropathy, dysarthria, and decreased lung function, among others. If unsure, please consult with your primary physician before making an appointment for Botox and always be sure to disclose medical history to aesthetic providers as well.
DSC Laser & Skin Care Center
(626)285-0800
www.dscbeauty.com
info@dscbeauty.com
889 S. San Gabriel Blvd. San Gabriel, CA 91776
